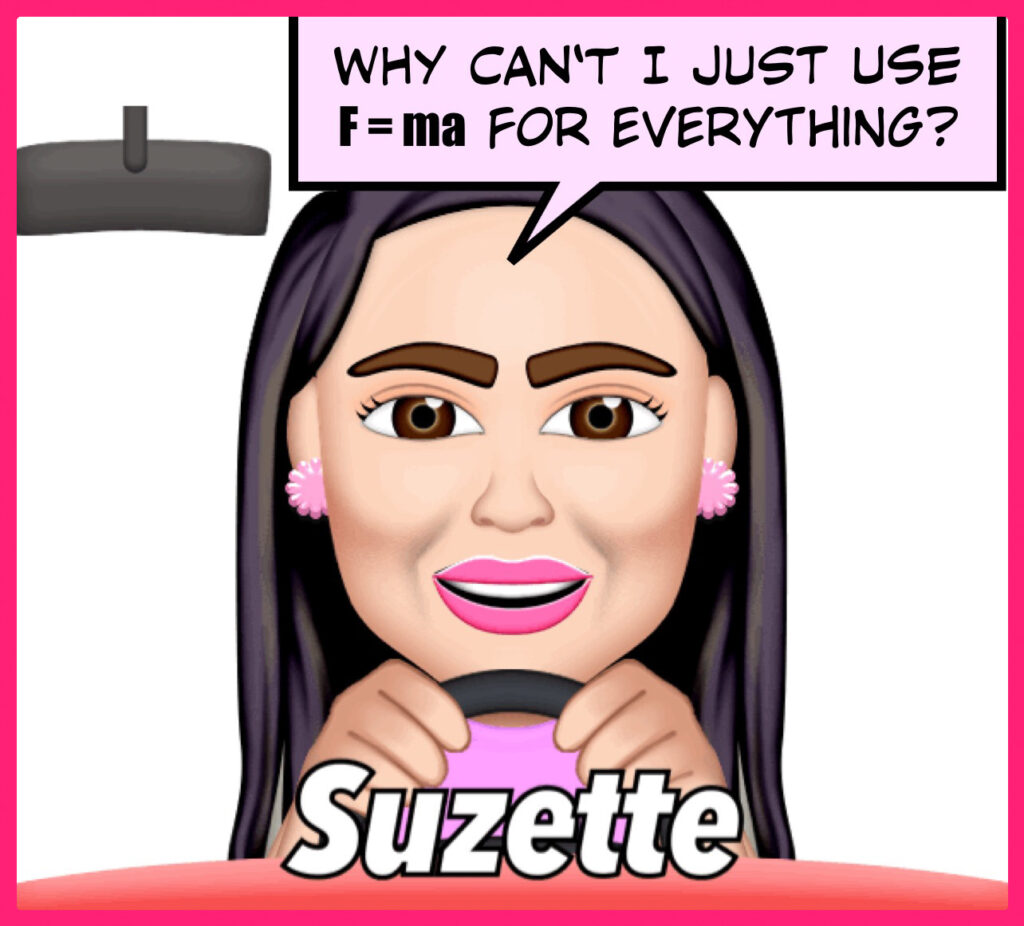

F = ma

We use cookies to help you navigate efficiently and perform certain functions. You will find detailed information about all cookies under each consent category below.
The cookies that are categorized as "Necessary" are stored on your browser as they are essential for enabling the basic functionalities of the site. ...
Necessary cookies are required to enable the basic features of this site, such as providing secure log-in or adjusting your consent preferences. These cookies do not store any personally identifiable data.
Functional cookies help perform certain functionalities like sharing the content of the website on social media platforms, collecting feedback, and other third-party features.
Analytical cookies are used to understand how visitors interact with the website. These cookies help provide information on metrics such as the number of visitors, bounce rate, traffic source, etc.
Performance cookies are used to understand and analyze the key performance indexes of the website which helps in delivering a better user experience for the visitors.
Advertisement cookies are used to provide visitors with customized advertisements based on the pages you visited previously and to analyze the effectiveness of the ad campaigns.



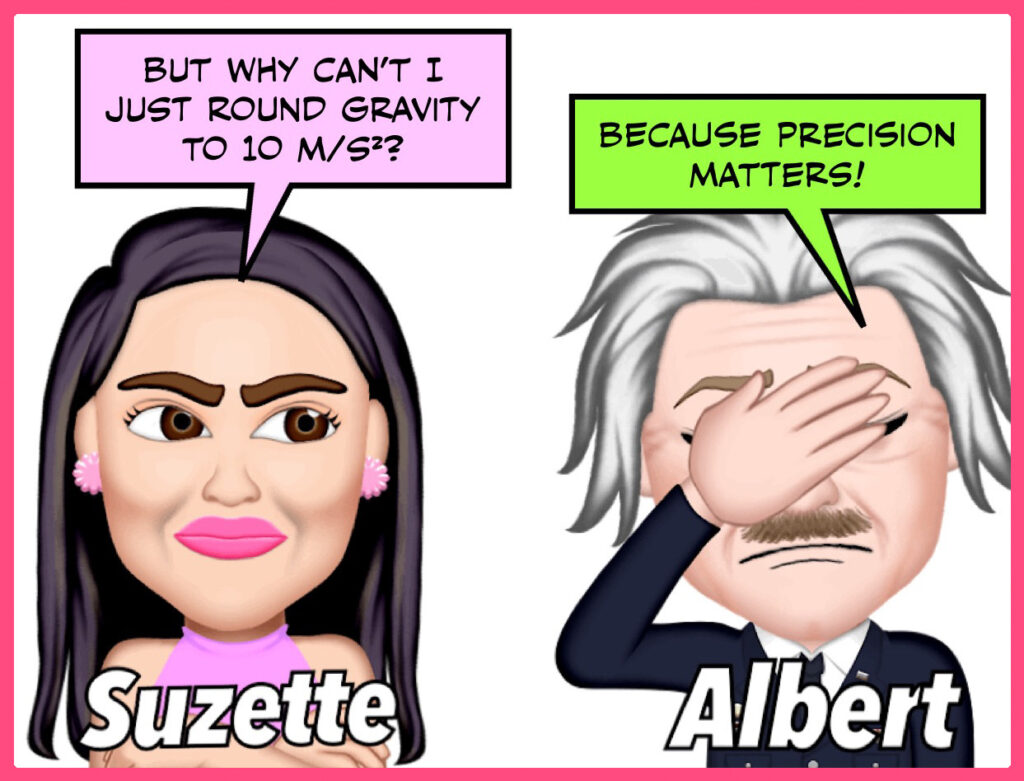
Explanation:
Suzette is asking why she can’t simplify her calculations by rounding the acceleration due to gravity (usually approximated as 9.8 m/s²) to a more convenient 10 m/s². Einstein responds that precision is crucial. In physics and other scientific disciplines, even small deviations from accurate values can lead to significant errors in calculations and experiments. Using precise values ensures reliability and accuracy in results, which is essential for scientific integrity. Thus, while rounding might seem easier, it can compromise the quality and correctness of the work.